What Is a Substance Said to Be if It Evaporates Easily?

Bromine liquid readily transitions to vapor at room temperature, indicating a loftier volatility.
In chemistry, volatility is a fabric quality which describes how readily a substance vaporizes. At a given temperature and pressure level, a substance with high volatility is more likely to exist as a vapour, while a substance with low volatility is more likely to be a liquid or solid. Volatility tin can also describe the trend of a vapor to condense into a liquid or solid; less volatile substances will more readily condense from a vapor than highly volatile ones.[1] Differences in volatility tin can be observed by comparison how fast substances within a grouping evaporate (or sublimate in the case of solids) when exposed to the atmosphere. A highly volatile substance such every bit rubbing alcohol (isopropyl alcohol) volition quickly evaporate, while a substance with low volatility such equally vegetable oil will remain condensed.[2] In general, solids are much less volatile than liquids, but there are some exceptions. Solids that sublimate (change straight from solid to vapor) such every bit dry out ice (solid carbon dioxide) or iodine can vaporize at a similar charge per unit equally some liquids under standard conditions.[3]
Clarification [edit]
Volatility itself has no divers numerical value, only it is often described using vapor pressures or boiling points (for liquids). High vapor pressures indicate a loftier volatility, while loftier humid points indicate low volatility. Vapor pressures and boiling points are ofttimes presented in tables and charts that tin can exist used to compare chemicals of interest. Volatility data is typically found through experimentation over a range of temperatures and pressures.
Vapor pressure [edit]
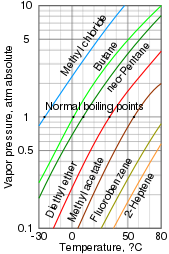
A log-lin vapor pressure chart for diverse liquids
Vapor pressure is a measurement of how readily a condensed phase forms a vapor at a given temperature. A substance enclosed in a sealed vessel initially at vacuum (no air within) will quickly fill whatever empty space with vapor. After the system reaches equilibrium and no more vapor is formed, this vapor pressure can be measured. Increasing the temperature increases the amount of vapor that is formed and thus the vapor pressure. In a mixture, each substance contributes to the overall vapor pressure of the mixture, with more than volatile compounds making a larger contribution.
Boiling betoken [edit]
Boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure level of a liquid is equal to the surrounding pressure, causing the liquid to rapidly evaporate, or boil. It is closely related to vapor pressure, but is dependent on pressure. The normal boiling point is the boiling betoken at atmospheric pressure, but it tin too be reported at college and lower pressures.[3]
Contributing factors [edit]
Intermolecular forces [edit]

Normal boiling bespeak (reddish) and melting point (blueish) of linear alkanes vs. number of carbon atoms.
An important factor influencing a substance's volatility is the strength of the interactions between its molecules. Attractive forces between molecules are what holds materials together, and materials with stronger intermolecular forces, such as near solids, are typically not very volatile. Ethanol and dimethyl ether, two chemicals with the aforementioned formula (C2H6O), accept different volatilities due to the different interactions that occur between their molecules in the liquid phase: ethanol molecules are capable of hydrogen bonding while dimethyl ether molecules are not.[four] The effect in an overall stronger attractive force between the ethanol molecules, making information technology the less volatile substance of the 2.
Molecular weight [edit]
In general, volatility tends to subtract with increasing molecular mass because larger molecules can participate in more intermolecular bonding,[5] although other factors such as structure and polarity play a significant function. The upshot of molecular mass can be partially isolated by comparing chemicals of like construction (i.e. esters, alkanes, etc.). For instance, linear alkanes exhibit decreasing volatility as the number of carbons in the concatenation increases.
Applications [edit]
Distillation [edit]

A rough oil distillation column.
Knowledge of volatility is oft useful in the separation of components from a mixture. When a mixture of condensed substances contains multiple substances with dissimilar levels of volatility, its temperature and pressure can exist manipulated such that the more volatile components change to a vapor while the less volatile substances remain in the liquid or solid phase. The newly formed vapor tin can so be discarded or condensed into a split up container. When the vapors are collected, this process is known as distillation.[half-dozen]
The process of petroleum refinement utilizes a technique known equally partial distillation, which allows several chemicals of varying volatility to be separated in a single stride. Crude oil entering a refinery is composed of many useful chemicals that need to exist separated. The crude oil flows into a distillation belfry and is heated upwards, which allows the more volatile components such as butane and kerosene to vaporize. These vapors motion up the belfry and eventually come in contact with cold surfaces, which causes them to condense and be collected. The most volatile chemical condense at the top of the column while the to the lowest degree volatile chemicals to vaporize condense in the lowest portion.[i] On the right is a picture illustrating the blueprint of a distillation belfry.
The departure in volatility between water and ethanol has traditionally been used in the refinement of drinking alcohol. In society to increase the concentration of ethanol in the production, alcohol makers would oestrus the initial booze mixture to a temperature where most of the ethanol vaporizes while most of the water remains liquid. The ethanol vapor is then collected and condensed in a separate container, resulting in a much more than concentrated product.[7]
Perfume [edit]
Volatility is an important consideration when crafting perfumes. Humans detect odors when aromatic vapors come up in contact with receptors in the nose. Ingredients that vaporize quickly later on being applied will produce fragrant vapors for a short fourth dimension before the oils evaporate. Slow-evaporating ingredients can stay on the skin for weeks or fifty-fifty months, but may not produce plenty vapors to produce a strong aroma. To preclude these problems, perfume designers advisedly consider the volatility of essential oils and other ingredients in their perfumes. Appropriate evaporation rates are achieved by modifying the corporeality of highly volatile and non-volatile ingredients used.[8]
See besides [edit]
- Clausius–Clapeyron relation
- Distillation
- Fractional distillation
- Fractional force per unit area
- Raoult'due south police
- Relative volatility
- Vapor–liquid equilibrium
- Volatile organic compound
References [edit]
- ^ a b Felder, Richard (2015). Uncomplicated Principles of Chemical Processes. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 279–281. ISBN978-1-119-17764-7.
- ^ Koretsky, Milo D. (2013). Engineering and Chemic Thermodynamics. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 639–641.
- ^ a b Zumdahl, Steven S. (2007). Chemistry . Houghton Mifflin. pp. 460-466. ISBN978-0-618-52844-8.
- ^ Atkins, Peter (2013). Chemical Principles. New York: West.H. Freeman and Company. pp. 368–369. ISBN978-1-319-07903-ane.
- ^ "Hydrocarbon boiling points". Retrieved 28 Apr 2021.
- ^ Armarego, Wilfred L. F. (2009). Purification of Laboratory Chemicals . Elsevier. pp. nine-12. ISBN978-one-85617-567-8.
- ^ Kvaalen, Eric. "Alcohol Distillation: Basic Principles, Equipment, Performance Relationships, and Condom". Purdue.
- ^ Sell, Charles (2006). The Chemistry of Fragrances . United kingdom: The Royal Order of Chemistry. pp. 200-202. ISBN978-0-85404-824-3.
External links [edit]
- Volatility from ilpi.com
- Definition of volatile from Wiktionary
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Volatility_(chemistry)
Post a Comment for "What Is a Substance Said to Be if It Evaporates Easily?"